Working with data matrices and analysis results
Source:vignettes/web/data-matrices-and-analysis-results.Rmd
data-matrices-and-analysis-results.RmdThis vignette will show the most suitable commands to retrieve data from a grandR object in different scenarios.
Throughout this vignette, we will be using the GRAND-SLAM processed SLAM-seq data set from Finkel et al. 2021 [3]. The data set contains time series (progressive labeling) samples from a human epithelial cell line (Calu3 cells); half of the samples were infected with SARS-CoV-2 for different periods of time. For more on these initial commands see the “Loading data” vignette.
sars <- ReadGRAND("https://zenodo.org/record/5834034/files/sars.tsv.gz",
design=c("Condition",Design$dur.4sU,Design$Replicate),
classify.genes = ClassifyGenes(name.unknown = "Viral"))Warning: Duplicate gene symbols (n=17, e.g. TXNRD3NB,ARL14EPL,PDE11A,HIST1H3D,SDHD,SOGA3)
present, making unique!
sars <- FilterGenes(sars) Data slots
Data is organized in an grandR object in so-called slots:
Slots(sars)[1] "count" "ntr" "alpha" "beta" To learn about metadata, see the loading data vignette. After loading GRAND-SLAM analysis results, the default slots are “count” (read counts), “ntr” (the new-to-total RNA ratio) and “alpha” and “beta” (the parameters for the Beta approximation of the NTR posterior distribution). Each of these slots contains a gene x columns (columns are either samples or cells, depending on whether your data is bulk or single cell data) matrix of numeric values.
There is also a default slot, which is used by many functions as default parameter.
DefaultSlot(sars)[1] "count"New slots are added by specific grandR functions such as
Normalize or NormalizeTPM, which, by default,
also change the default slot. The default slot can also be set
manually:
sars <- Normalize(sars)
DefaultSlot(sars)[1] "norm"
DefaultSlot(sars)<-"count"
DefaultSlot(sars)[1] "count"
sars <- NormalizeTPM(sars,set.to.default = FALSE)
DefaultSlot(sars)[1] "count"
DefaultSlot(sars)<-"norm"There are also other grandR functions that add additional slots, but
do not update the DefaultSlot automatically:
sars <- ComputeNtrCI(sars)
DefaultSlot(sars)[1] "norm"
Slots(sars)[1] "count" "ntr" "alpha" "beta" "norm" "tpm" "lower" "upper"Analyses
In addition to data slots, there is an additional kind of data that is part of a grandR object: analyses.
Analyses(sars)NULLAfter loading data there are no analyses, but such data are added e.g. by performing modeling of progressive labeling time courses or analyzing differential gene expression (see the vignettes Kinetic modeling and Differential expression for more on these):
SetParallel(cores = 2) # increase 2 on your system, or omit the cores = 2 for automatic detectionNULL
sars <- FitKinetics(sars,name="kinetics",steady.state=c(Mock=TRUE,SARS=FALSE))
sars <- LFC(sars,contrasts=GetContrasts(sars,contrast = c("duration.4sU.original","no4sU"),
group = "Condition",no4sU=TRUE))
Analyses(sars) [1] "kinetics.Mock" "kinetics.SARS" "total.1h vs no4sU.Mock"
[4] "total.2h vs no4sU.Mock" "total.3h vs no4sU.Mock" "total.4h vs no4sU.Mock"
[7] "total.1h vs no4sU.SARS" "total.2h vs no4sU.SARS" "total.3h vs no4sU.SARS"
[10] "total.4h vs no4sU.SARS"Both analysis methods, FitKinetics and LFC
added multiple analyses: FitKinetics added an analysis for
each Condition whereas LFC added an analysis
for each of many pairwise comparison defined by
GetContrasts (see Differential expression for
details).
What is common to data slots and analyses is that both are tables with as many rows as there are genes. What is different is that the columns of data slots always correspond to the samples or cells (depending on whether data are bulk or single cell data), and the columns of analysis tables are arbitrary and depend on the kind of analysis performed.
Analysis columns can be retrieved by setting the description
parameter to TRUE for Analyses:
Analyses(sars,description = TRUE)$kinetics.Mock
[1] "Synthesis" "Half-life"
$kinetics.SARS
[1] "Synthesis" "Half-life"
$`total.1h vs no4sU.Mock`
[1] "LFC" "M"
$`total.2h vs no4sU.Mock`
[1] "LFC" "M"
$`total.3h vs no4sU.Mock`
[1] "LFC" "M"
$`total.4h vs no4sU.Mock`
[1] "LFC" "M"
$`total.1h vs no4sU.SARS`
[1] "LFC" "M"
$`total.2h vs no4sU.SARS`
[1] "LFC" "M"
$`total.3h vs no4sU.SARS`
[1] "LFC" "M"
$`total.4h vs no4sU.SARS`
[1] "LFC" "M" We see that the FitKinetics function by default creates
tables with two columns (Synthesis and
Half-life) corresponding to the synthesis rate and RNA
half-life for each gene, and the LFC function creates a
single column called LFC corresponding to the log2 fold
change for each gene.
Retrieving data from slots or analyses
There are essentially three functions you can use for retrieving slot data:
-
GetTable: The swiss army knive, returns a data frame with genes as rows and columns made from potentially several slots and/or analyses; usually for all or at least a lot of genes -
GetData: Returns a data frame with the samples or cells as rows and slot data for particular genes in columns; usually for a single or at most very few genes -
GetAnalysisTable: Returns a data frame with genes as rows and columns made from potentially several analyses; usually for all or at least a lot of genes; there is (almost) no need to call this function (see below for exceptions)
GetTable
Without any other parameters GetTable returns data for
all genes from the default slot:
head(GetTable(sars)) Mock.no4sU.A Mock.1h.A Mock.2h.A Mock.2h.B Mock.3h.A Mock.4h.A SARS.no4sU.A SARS.1h.A
MIB2 50.61593 138.9483 152.6633 100.2339 116.0365 127.5967 175.5632 210.7226
OSBPL9 480.85133 397.6568 386.5828 466.7414 429.5386 421.7695 476.5287 407.3970
BTF3L4 578.46777 399.6418 302.8643 545.1853 526.9991 417.5061 501.6091 431.9813
ZFYVE9 184.38660 160.7831 157.1775 158.6311 127.9964 131.8601 238.2643 193.1624
PRPF38A 357.92693 310.3179 335.6951 364.7643 329.7880 362.6913 501.6091 278.6221
AHCYL1 708.62302 569.6881 581.9262 707.7386 641.7633 653.5143 589.3907 361.7405
SARS.2h.A SARS.2h.B SARS.3h.A SARS.4h.A
MIB2 275.4692 190.0241 231.7082 191.9265
OSBPL9 399.1705 435.3603 340.6110 348.1020
BTF3L4 269.2322 446.9580 382.3185 398.9061
ZFYVE9 168.4001 210.5431 192.3178 203.2163
PRPF38A 309.7730 365.7740 315.1231 312.3510
AHCYL1 384.6174 410.3806 421.7089 423.3673You can change the slot by specifying another type
parameter:
head(GetTable(sars,type="count")) Mock.no4sU.A Mock.1h.A Mock.2h.A Mock.2h.B Mock.3h.A Mock.4h.A SARS.no4sU.A SARS.1h.A
MIB2 14 420 372 230 456 419 14 180
OSBPL9 133 1202 942 1071 1688 1385 38 348
BTF3L4 160 1208 738 1251 2071 1371 40 369
ZFYVE9 51 486 383 364 503 433 19 165
PRPF38A 99 938 818 837 1296 1191 40 238
AHCYL1 196 1722 1418 1624 2522 2146 47 309
SARS.2h.A SARS.2h.B SARS.3h.A SARS.4h.A
MIB2 265 213 100 102
OSBPL9 384 488 147 185
BTF3L4 259 501 165 212
ZFYVE9 162 236 83 108
PRPF38A 298 410 136 166
AHCYL1 370 460 182 225You can use multiple slots (we only show the column names instead of
the head of the returned table):
[1] "Mock.no4sU.A.norm" "Mock.1h.A.norm" "Mock.2h.A.norm" "Mock.2h.B.norm"
[5] "Mock.3h.A.norm" "Mock.4h.A.norm" "SARS.no4sU.A.norm" "SARS.1h.A.norm"
[9] "SARS.2h.A.norm" "SARS.2h.B.norm" "SARS.3h.A.norm" "SARS.4h.A.norm"
[13] "Mock.no4sU.A.count" "Mock.1h.A.count" "Mock.2h.A.count" "Mock.2h.B.count"
[17] "Mock.3h.A.count" "Mock.4h.A.count" "SARS.no4sU.A.count" "SARS.1h.A.count"
[21] "SARS.2h.A.count" "SARS.2h.B.count" "SARS.3h.A.count" "SARS.4h.A.count" By using the mode.slot syntax (mode being either of
total,new and old), you can also
retrieve new RNA counts or new RNA normalized values:
head(GetTable(sars,type="new.norm")) Mock.no4sU.A Mock.1h.A Mock.2h.A Mock.2h.B Mock.3h.A Mock.4h.A SARS.no4sU.A SARS.1h.A
MIB2 NA 2.334332 32.10509 16.46843 40.35750 52.62088 NA 10.325408
OSBPL9 NA 17.337839 55.16537 62.35665 82.90096 109.74443 NA 49.254301
BTF3L4 NA 17.304491 69.29534 120.86759 177.28251 223.49103 NA 40.303858
ZFYVE9 NA 2.267041 27.86758 25.77755 39.24370 68.76503 NA 3.283761
PRPF38A NA 28.735438 122.15944 133.94145 160.30993 252.36062 NA 82.304970
AHCYL1 NA 12.988889 66.68874 59.59159 88.56334 117.43653 NA 14.469619
SARS.2h.A SARS.2h.B SARS.3h.A SARS.4h.A
MIB2 68.12354 38.99294 110.7333 116.5570
OSBPL9 154.35924 181.37111 169.2155 224.5606
BTF3L4 101.58131 177.39764 194.9442 232.5622
ZFYVE9 56.46454 66.65795 100.9091 144.2633
PRPF38A 223.16044 235.55848 231.8361 284.3331
AHCYL1 134.00072 139.28318 214.9450 262.4454Note that the no4sU columns only have NA values. You can change this
behavior by specifying the ntr.na parameter:
head(GetTable(sars,type="new.norm",ntr.na = FALSE)) Mock.no4sU.A Mock.1h.A Mock.2h.A Mock.2h.B Mock.3h.A Mock.4h.A SARS.no4sU.A SARS.1h.A
MIB2 0 2.334332 32.10509 16.46843 40.35750 52.62088 0 10.325408
OSBPL9 0 17.337839 55.16537 62.35665 82.90096 109.74443 0 49.254301
BTF3L4 0 17.304491 69.29534 120.86759 177.28251 223.49103 0 40.303858
ZFYVE9 0 2.267041 27.86758 25.77755 39.24370 68.76503 0 3.283761
PRPF38A 0 28.735438 122.15944 133.94145 160.30993 252.36062 0 82.304970
AHCYL1 0 12.988889 66.68874 59.59159 88.56334 117.43653 0 14.469619
SARS.2h.A SARS.2h.B SARS.3h.A SARS.4h.A
MIB2 68.12354 38.99294 110.7333 116.5570
OSBPL9 154.35924 181.37111 169.2155 224.5606
BTF3L4 101.58131 177.39764 194.9442 232.5622
ZFYVE9 56.46454 66.65795 100.9091 144.2633
PRPF38A 223.16044 235.55848 231.8361 284.3331
AHCYL1 134.00072 139.28318 214.9450 262.4454GetTable can also be used to retrieve analysis
results:
head(GetTable(sars,type="kinetics")) kinetics.Mock.Synthesis kinetics.Mock.Half-life kinetics.SARS.Synthesis
MIB2 11.44548 6.685331 37.37293
OSBPL9 33.88277 8.936141 100.12116
BTF3L4 75.16929 4.453564 98.62337
ZFYVE9 22.06668 5.129308 49.96790
PRPF38A 84.46720 2.891519 204.62499
AHCYL1 33.58576 13.390102 106.41401
kinetics.SARS.Half-life
MIB2 4.6532263
OSBPL9 2.0838946
BTF3L4 2.0688530
ZFYVE9 2.2536813
PRPF38A 0.9362758
AHCYL1 1.9559446Note that you do not have to specify the full name (it actually is a regular expression that is matched against each analysis name).
It is also easily possible to only retrieve data for specific columns
(i.e., samples or cells) by using the columns parameter.
Note that you can use names from the Coldata table to
construct a logical vector over the columns; using a character vector
(to specify names) or a numeric vector (to specify positions) also
works:
head(GetTable(sars,columns=duration.4sU>=2 & Condition=="Mock")) Mock.2h.A Mock.2h.B Mock.3h.A Mock.4h.A
MIB2 152.6633 100.2339 116.0365 127.5967
OSBPL9 386.5828 466.7414 429.5386 421.7695
BTF3L4 302.8643 545.1853 526.9991 417.5061
ZFYVE9 157.1775 158.6311 127.9964 131.8601
PRPF38A 335.6951 364.7643 329.7880 362.6913
AHCYL1 581.9262 707.7386 641.7633 653.5143 Mock.no4sU.A SARS.no4sU.A
MIB2 50.61593 175.5632
OSBPL9 480.85133 476.5287
BTF3L4 578.46777 501.6091
ZFYVE9 184.38660 238.2643
PRPF38A 357.92693 501.6091
AHCYL1 708.62302 589.3907
head(GetTable(sars,columns=4:6)) Mock.2h.B Mock.3h.A Mock.4h.A
MIB2 100.2339 116.0365 127.5967
OSBPL9 466.7414 429.5386 421.7695
BTF3L4 545.1853 526.9991 417.5061
ZFYVE9 158.6311 127.9964 131.8601
PRPF38A 364.7643 329.7880 362.6913
AHCYL1 707.7386 641.7633 653.5143It is furthermore possible to only fetch data for specific genes,
e.g. viral genes using the genes parameter. It is either a
logical vector, a numeric vector, or gene names/symbols:
GetTable(sars,genes=GeneInfo(sars,"Type")=="Viral") Mock.no4sU.A Mock.1h.A Mock.2h.A Mock.2h.B Mock.3h.A Mock.4h.A SARS.no4sU.A SARS.1h.A
ORF3a 705.0076 567.3723 807.2277 577.8703 574.3298 570.3785 2083095 218342.6
E 423.0046 343.4008 471.1222 336.4373 326.7344 328.5843 1169941 121044.9
M 1974.0213 1531.0781 2081.0633 1585.4390 1504.9121 1485.1768 5267423 552293.4
ORF6 473.6205 428.4240 536.7838 410.0874 402.3108 387.3580 1775044 166706.2
ORF7a 1142.4738 864.1262 1186.4236 892.5176 855.0058 836.5349 3535316 313785.9
ORF7b 719.4693 502.1989 677.1356 503.7844 468.7264 470.1893 1860092 190325.8
ORF8 1822.1735 1316.0390 1731.4151 1287.3521 1222.9637 1209.8847 4927896 456242.5
N 8843.3260 7476.4119 10056.0785 7570.2752 7072.8831 7040.9623 25288888 2505283.4
ORF10 1663.0948 1425.5436 1843.8606 1420.2710 1323.2233 1297.5884 5242405 522616.6
ORF1ab 1659.4794 1462.5964 1874.2291 1472.1311 1389.1300 1366.1069 4954281 628565.6
S 965.3181 836.9982 1090.3934 828.4551 779.1750 766.4938 3405763 335616.7
SARS.2h.A SARS.2h.B SARS.3h.A SARS.4h.A
ORF3a 606628.0 784826.2 1246796.1 1507097.3
E 328393.6 467000.7 759154.7 950348.6
M 1647309.2 1968405.8 3039142.1 3810695.3
ORF6 506668.0 551540.9 788120.5 985535.1
ORF7a 872093.0 1217287.1 1703059.6 2043968.5
ORF7b 489639.8 712069.3 1086081.0 1301399.1
ORF8 1341787.8 1795438.4 2533144.8 3068775.1
N 9100887.5 9091438.6 12024874.9 14564147.9
ORF10 1723751.4 1748268.8 2504647.0 3128464.3
ORF1ab 1404586.5 2085797.9 2881680.2 3340669.1
S 811972.1 1160304.8 1635192.3 1968855.6
GetTable(sars,genes=1:3) Mock.no4sU.A Mock.1h.A Mock.2h.A Mock.2h.B Mock.3h.A Mock.4h.A SARS.no4sU.A SARS.1h.A
MIB2 50.61593 138.9483 152.6633 100.2339 116.0365 127.5967 175.5632 210.7226
OSBPL9 480.85133 397.6568 386.5828 466.7414 429.5386 421.7695 476.5287 407.3970
BTF3L4 578.46777 399.6418 302.8643 545.1853 526.9991 417.5061 501.6091 431.9813
SARS.2h.A SARS.2h.B SARS.3h.A SARS.4h.A
MIB2 275.4692 190.0241 231.7082 191.9265
OSBPL9 399.1705 435.3603 340.6110 348.1020
BTF3L4 269.2322 446.9580 382.3185 398.9061
GetTable(sars,genes="MYC") Mock.no4sU.A Mock.1h.A Mock.2h.A Mock.2h.B Mock.3h.A Mock.4h.A SARS.no4sU.A SARS.1h.A
MYC 1547.401 1577.394 2542.747 1927.106 2126.318 2047.333 3436.023 2231.318
SARS.2h.A SARS.2h.B SARS.3h.A SARS.4h.A
MYC 5206.889 3753.198 4386.235 4340.926Sometimes, it makes sense to add the GeneInfo table (for
more on gene metadata, see the loading data
vignette):
df <- GetTable(sars,type="norm",gene.info = TRUE)
head(df) Gene Symbol Length Type Mock.no4sU.A Mock.1h.A Mock.2h.A Mock.2h.B
MIB2 ENSG00000197530 MIB2 4247 Cellular 50.61593 138.9483 152.6633 100.2339
OSBPL9 ENSG00000117859 OSBPL9 4520 Cellular 480.85133 397.6568 386.5828 466.7414
BTF3L4 ENSG00000134717 BTF3L4 4703 Cellular 578.46777 399.6418 302.8643 545.1853
ZFYVE9 ENSG00000157077 ZFYVE9 5194 Cellular 184.38660 160.7831 157.1775 158.6311
PRPF38A ENSG00000134748 PRPF38A 5274 Cellular 357.92693 310.3179 335.6951 364.7643
AHCYL1 ENSG00000168710 AHCYL1 4313 Cellular 708.62302 569.6881 581.9262 707.7386
Mock.3h.A Mock.4h.A SARS.no4sU.A SARS.1h.A SARS.2h.A SARS.2h.B SARS.3h.A SARS.4h.A
MIB2 116.0365 127.5967 175.5632 210.7226 275.4692 190.0241 231.7082 191.9265
OSBPL9 429.5386 421.7695 476.5287 407.3970 399.1705 435.3603 340.6110 348.1020
BTF3L4 526.9991 417.5061 501.6091 431.9813 269.2322 446.9580 382.3185 398.9061
ZFYVE9 127.9964 131.8601 238.2643 193.1624 168.4001 210.5431 192.3178 203.2163
PRPF38A 329.7880 362.6913 501.6091 278.6221 309.7730 365.7740 315.1231 312.3510
AHCYL1 641.7633 653.5143 589.3907 361.7405 384.6174 410.3806 421.7089 423.3673
ggplot(df,aes(`SARS.4h.A`,`SARS.no4sU.A`,color=Type))+
geom_point()+
scale_x_log10()+
scale_y_log10()+
geom_abline()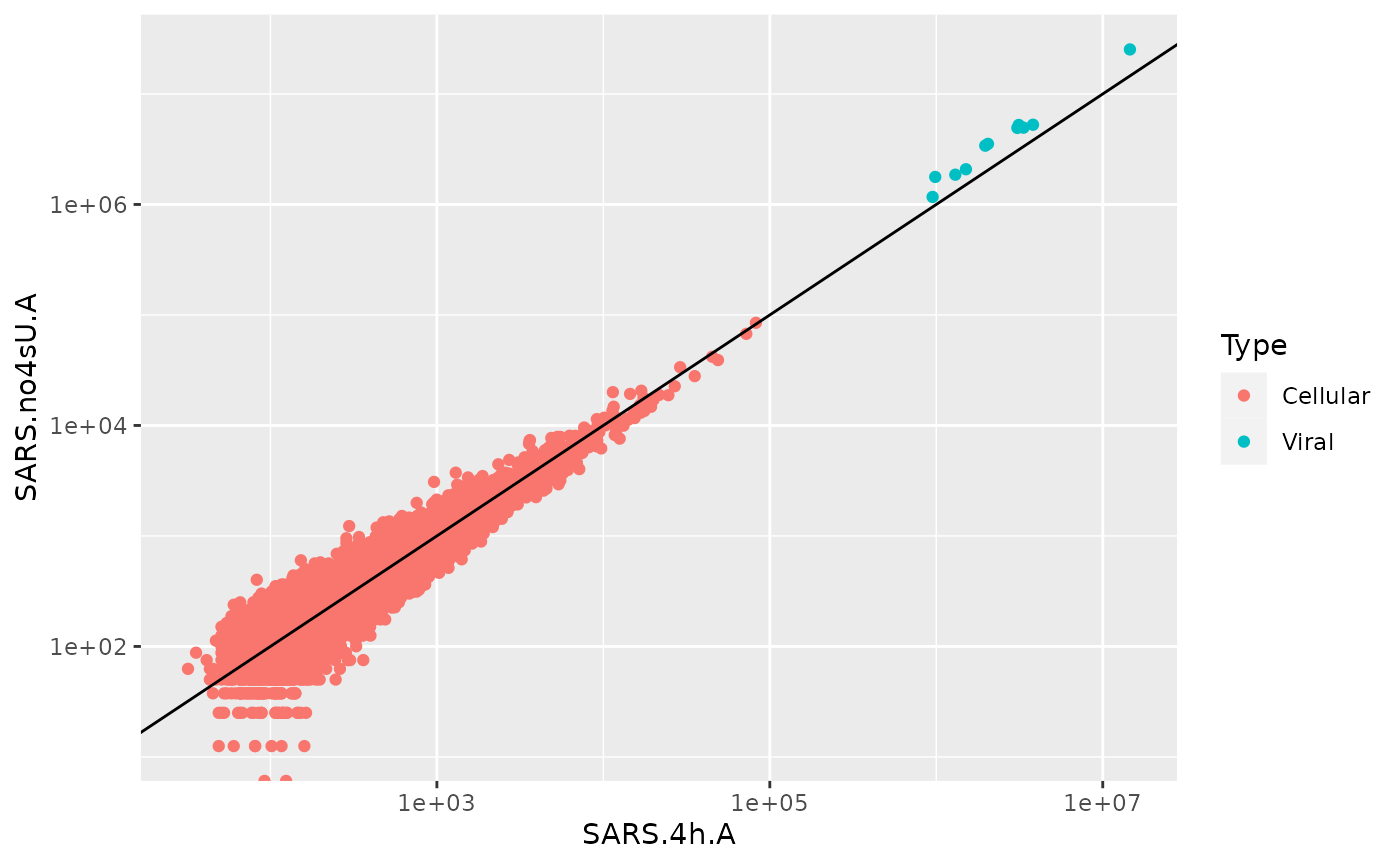
Finally, it is also straight-forward to get summarized values across
samples or cells from the same Condition:
head(GetTable(sars,summarize = TRUE)) Mock SARS
MIB2 127.0957 219.9701
OSBPL9 420.4578 386.1282
BTF3L4 438.4393 385.8792
ZFYVE9 147.2896 193.5279
PRPF38A 340.6513 316.3286
AHCYL1 630.9261 400.3629This is accomplished by a “summarize matrix”:
smat <- GetSummarizeMatrix(sars)
smat Mock SARS
Mock.no4sU.A 0.0 0.0
Mock.1h.A 0.2 0.0
Mock.2h.A 0.2 0.0
Mock.2h.B 0.2 0.0
Mock.3h.A 0.2 0.0
Mock.4h.A 0.2 0.0
SARS.no4sU.A 0.0 0.0
SARS.1h.A 0.0 0.2
SARS.2h.A 0.0 0.2
SARS.2h.B 0.0 0.2
SARS.3h.A 0.0 0.2
SARS.4h.A 0.0 0.2Instead of specifying TRUE for the summarize parameter,
you can also specify such a matrix:
head(GetTable(sars,summarize = smat)) Mock SARS
MIB2 127.0957 219.9701
OSBPL9 420.4578 386.1282
BTF3L4 438.4393 385.8792
ZFYVE9 147.2896 193.5279
PRPF38A 340.6513 316.3286
AHCYL1 630.9261 400.3629For summarization, the summarize matrix is matrix-multiplied with the
raw matrix. GetSummarizeMatrix will generate a matrix with
columns corresponding to Conditions:
Condition(sars) [1] Mock Mock Mock Mock Mock Mock SARS SARS SARS SARS SARS SARS
Levels: Mock SARSBy default, no4sU columns are removed (i.e. zero in the matrix), but the no4sU parameter can change this:
GetSummarizeMatrix(sars,no4sU = TRUE) Mock SARS
Mock.no4sU.A 0.1666667 0.0000000
Mock.1h.A 0.1666667 0.0000000
Mock.2h.A 0.1666667 0.0000000
Mock.2h.B 0.1666667 0.0000000
Mock.3h.A 0.1666667 0.0000000
Mock.4h.A 0.1666667 0.0000000
SARS.no4sU.A 0.0000000 0.1666667
SARS.1h.A 0.0000000 0.1666667
SARS.2h.A 0.0000000 0.1666667
SARS.2h.B 0.0000000 0.1666667
SARS.3h.A 0.0000000 0.1666667
SARS.4h.A 0.0000000 0.1666667It is also possible to focus on specific columns (samples or cells) only:
GetSummarizeMatrix(sars,columns = duration.4sU<4) Mock SARS
Mock.no4sU.A 0.00 0.00
Mock.1h.A 0.25 0.00
Mock.2h.A 0.25 0.00
Mock.2h.B 0.25 0.00
Mock.3h.A 0.25 0.00
Mock.4h.A 0.00 0.00
SARS.no4sU.A 0.00 0.00
SARS.1h.A 0.00 0.25
SARS.2h.A 0.00 0.25
SARS.2h.B 0.00 0.25
SARS.3h.A 0.00 0.25
SARS.4h.A 0.00 0.00The default behavior is to compute the average, this can be change to computing sums:
GetSummarizeMatrix(sars,average = FALSE) Mock SARS
Mock.no4sU.A 0 0
Mock.1h.A 1 0
Mock.2h.A 1 0
Mock.2h.B 1 0
Mock.3h.A 1 0
Mock.4h.A 1 0
SARS.no4sU.A 0 0
SARS.1h.A 0 1
SARS.2h.A 0 1
SARS.2h.B 0 1
SARS.3h.A 0 1
SARS.4h.A 0 1As a final example, to get averaged normalized expression values for the 2h timepoint only:
head(GetTable(sars,summarize = GetSummarizeMatrix(sars,columns=duration.4sU==2))) Mock SARS
MIB2 126.4486 232.7467
OSBPL9 426.6621 417.2654
BTF3L4 424.0248 358.0951
ZFYVE9 157.9043 189.4716
PRPF38A 350.2297 337.7735
AHCYL1 644.8324 397.4990GetData
GetData is the little cousin of GetTable:
It returns a data frame with the samples or cells as rows and slot data
for either a single gene or very few genes:
GetData(sars,genes="MYC") Name Condition Replicate duration.4sU duration.4sU.original no4sU
Mock.no4sU.A Mock.no4sU.A Mock A 0 no4sU TRUE
Mock.1h.A Mock.1h.A Mock A 1 1h FALSE
Mock.2h.A Mock.2h.A Mock A 2 2h FALSE
Mock.2h.B Mock.2h.B Mock B 2 2h FALSE
Mock.3h.A Mock.3h.A Mock A 3 3h FALSE
Mock.4h.A Mock.4h.A Mock A 4 4h FALSE
SARS.no4sU.A SARS.no4sU.A SARS A 0 no4sU TRUE
SARS.1h.A SARS.1h.A SARS A 1 1h FALSE
SARS.2h.A SARS.2h.A SARS A 2 2h FALSE
SARS.2h.B SARS.2h.B SARS B 2 2h FALSE
SARS.3h.A SARS.3h.A SARS A 3 3h FALSE
SARS.4h.A SARS.4h.A SARS A 4 4h FALSE
Value
Mock.no4sU.A 1547.401
Mock.1h.A 1577.394
Mock.2h.A 2542.747
Mock.2h.B 1927.106
Mock.3h.A 2126.318
Mock.4h.A 2047.333
SARS.no4sU.A 3436.023
SARS.1h.A 2231.318
SARS.2h.A 5206.889
SARS.2h.B 3753.198
SARS.3h.A 4386.235
SARS.4h.A 4340.926Note that by default, the Coldata table is also added
(for more on column metadata, see the loading data vignette). Note that in
contrast to GetTable, where you can add the
GeneInfo table, i.e. gene metadata, here it is the columns
metadata! This can be changed by using the coldata
parameter:
GetData(sars,genes="MYC",coldata = FALSE) Value
Mock.no4sU.A 1547.401
Mock.1h.A 1577.394
Mock.2h.A 2542.747
Mock.2h.B 1927.106
Mock.3h.A 2126.318
Mock.4h.A 2047.333
SARS.no4sU.A 3436.023
SARS.1h.A 2231.318
SARS.2h.A 5206.889
SARS.2h.B 3753.198
SARS.3h.A 4386.235
SARS.4h.A 4340.926It is also possible to retrieve data for multiple genes and/or multiple slots, and to restrict the columns:
# multiple genes
GetData(sars,genes=c("MYC","SRSF6"),columns=Condition=="Mock",coldata = FALSE) MYC SRSF6
Mock.no4sU.A 1547.401 1326.860
Mock.1h.A 1577.394 1193.301
Mock.2h.A 2542.747 1219.665
Mock.2h.B 1927.106 1425.936
Mock.3h.A 2126.318 1207.950
Mock.4h.A 2047.333 1156.897
# multiple slots, as above, compute also for no4sU samples instead of NA
GetData(sars,mode.slot=c("new.norm","old.norm"),genes="MYC",
columns=Condition=="Mock",coldata = FALSE, ntr.na = FALSE) new.norm old.norm
Mock.no4sU.A 0.0000 1547.4013
Mock.1h.A 979.0886 598.3056
Mock.2h.A 2542.7466 0.0000
Mock.2h.B 1927.1059 0.0000
Mock.3h.A 2126.3181 0.0000
Mock.4h.A 2047.3331 0.0000
# multiple genes and slots
GetData(sars,mode.slot=c("count","norm"),genes=c("MYC","SRSF6"),
columns=Condition=="Mock",coldata = FALSE) MYC.count SRSF6.count MYC.norm SRSF6.norm
Mock.no4sU.A 428 367 1547.401 1326.860
Mock.1h.A 4768 3607 1577.394 1193.301
Mock.2h.A 6196 2972 2542.747 1219.665
Mock.2h.B 4422 3272 1927.106 1425.936
Mock.3h.A 8356 4747 2126.318 1207.950
Mock.4h.A 6723 3799 2047.333 1156.897Finally, it is also possible to append multiple genes (and/or slots) not as columns, but as additional rows:
GetData(sars,genes=c("MYC","SRSF6"),columns=duration.4sU<2,by.rows = TRUE) Name Condition Replicate duration.4sU duration.4sU.original no4sU Gene Value
1 Mock.no4sU.A Mock A 0 no4sU TRUE MYC 1547.401
2 Mock.1h.A Mock A 1 1h FALSE MYC 1577.394
3 SARS.no4sU.A SARS A 0 no4sU TRUE MYC 3436.023
4 SARS.1h.A SARS A 1 1h FALSE MYC 2231.318
5 Mock.no4sU.A Mock A 0 no4sU TRUE SRSF6 1326.860
6 Mock.1h.A Mock A 1 1h FALSE SRSF6 1193.301
7 SARS.no4sU.A SARS A 0 no4sU TRUE SRSF6 2370.103
8 SARS.1h.A SARS A 1 1h FALSE SRSF6 1616.711This can be quite helpful, as for the following example: We retrieve total, old and new RNA for SRSF6 (only replicate A), and do this by rows. This way, the data can directly be used for ggplot to plot the progressive labeling time course (note the much shorter half-life, which is the time where the new and old lines cross, for SARS as compared to Mock):
df <- GetData(sars,mode.slot=c("old.norm","new.norm","total.norm"),genes="SRSF6",
columns=Replicate=="A",by.rows = TRUE)
ggplot(df,aes(duration.4sU,Value,color=mode.slot))+
geom_line()+
facet_wrap(~Condition)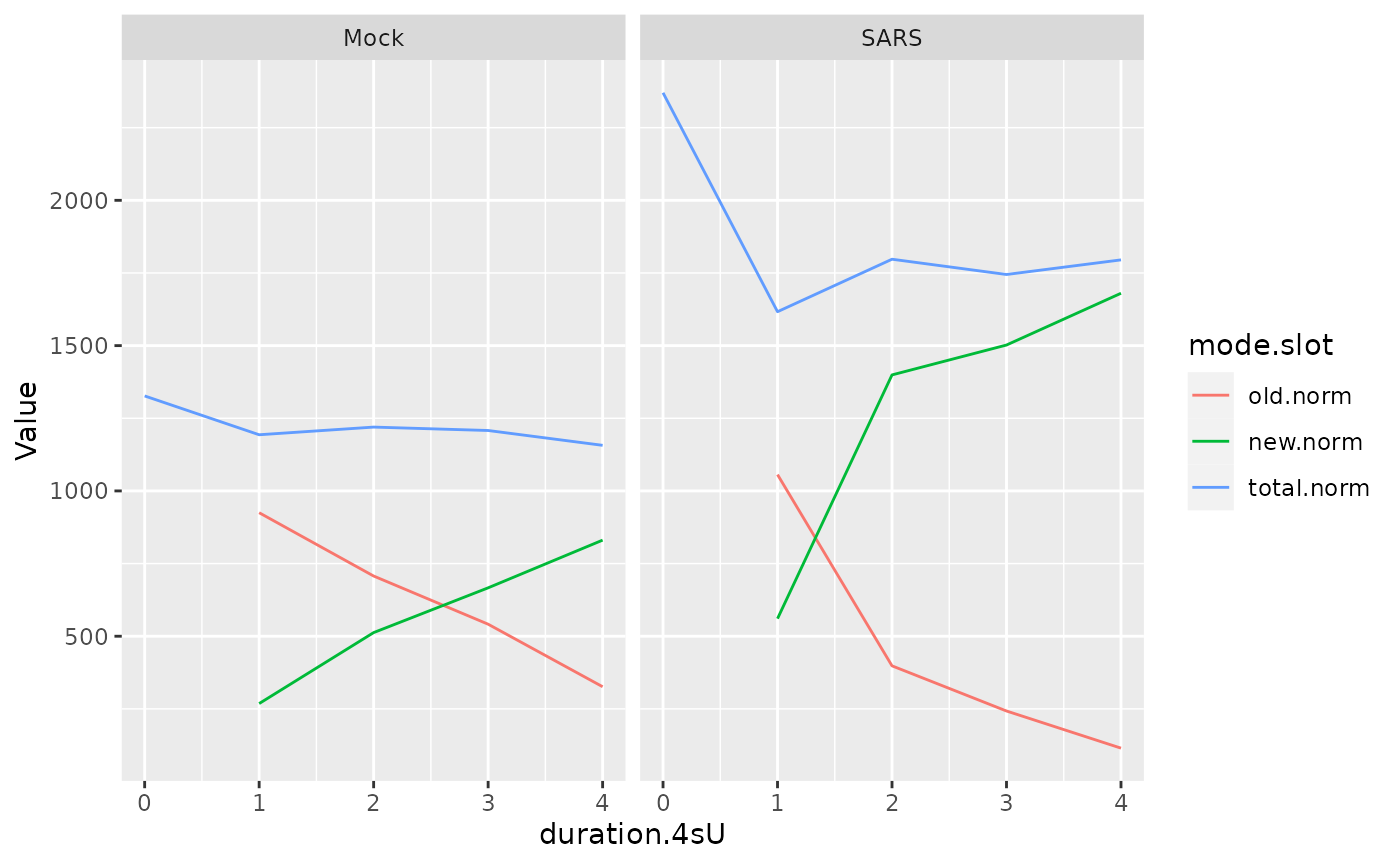
GetAnalysisTable
As indicated above, GetTable can also be used to
retrieve analysis results. However, sometimes it is better to be
explicit when coding analysis scripts, and you can use
GetAnalysisTable instead. Furthermore, there are two
additional benefits of GetAnalysisTable over
GetTable: First, by default, the prefix for each column of
the returned table is the analysis name, which cannot be turned off when
using GetTable (also note that the GeneInfo
table is added by default for GetAnalysisTable, can be
turned off by setting the gene.info parameter to FALSE)
head(GetTable(sars,"kinetics.Mock")) kinetics.Mock.Synthesis kinetics.Mock.Half-life
MIB2 11.44548 6.685331
OSBPL9 33.88277 8.936141
BTF3L4 75.16929 4.453564
ZFYVE9 22.06668 5.129308
PRPF38A 84.46720 2.891519
AHCYL1 33.58576 13.390102
head(GetAnalysisTable(sars,"kinetics.Mock")) Gene Symbol Length Type kinetics.Mock.Synthesis
MIB2 ENSG00000197530 MIB2 4247 Cellular 11.44548
OSBPL9 ENSG00000117859 OSBPL9 4520 Cellular 33.88277
BTF3L4 ENSG00000134717 BTF3L4 4703 Cellular 75.16929
ZFYVE9 ENSG00000157077 ZFYVE9 5194 Cellular 22.06668
PRPF38A ENSG00000134748 PRPF38A 5274 Cellular 84.46720
AHCYL1 ENSG00000168710 AHCYL1 4313 Cellular 33.58576
kinetics.Mock.Half-life
MIB2 6.685331
OSBPL9 8.936141
BTF3L4 4.453564
ZFYVE9 5.129308
PRPF38A 2.891519
AHCYL1 13.390102
head(GetAnalysisTable(sars,"kinetics.Mock",prefix.by.analysis = FALSE)) Gene Symbol Length Type Synthesis Half-life
MIB2 ENSG00000197530 MIB2 4247 Cellular 11.44548 6.685331
OSBPL9 ENSG00000117859 OSBPL9 4520 Cellular 33.88277 8.936141
BTF3L4 ENSG00000134717 BTF3L4 4703 Cellular 75.16929 4.453564
ZFYVE9 ENSG00000157077 ZFYVE9 5194 Cellular 22.06668 5.129308
PRPF38A ENSG00000134748 PRPF38A 5274 Cellular 84.46720 2.891519
AHCYL1 ENSG00000168710 AHCYL1 4313 Cellular 33.58576 13.390102Turning off the prefixes might sound like a minor aesthetic surgery, but is quite important in some cases. Imagine you want to fit the kinetic model (i) for the full time course (as we have already done) and (ii) after removing some time points:
restricted <- subset(sars,columns = duration.4sU!=1)
restricted <- FitKinetics(restricted,name="restricted",steady.state=c(Mock=TRUE,SARS=FALSE))And now you want to put these analyses back into the original
sars object for comparison. You can use the
AddAnalysis function, but here it is important not to add
the prefixes for consistency:
# we need to omit prefixes and gene info, since the analysis table to be added
# should have columns Synthesis and Half-life only
mock.tab <- GetAnalysisTable(restricted,analyses="restricted.Mock",
prefix.by.analysis = FALSE,gene.info = FALSE)
sars.tab <- GetAnalysisTable(restricted,analyses="restricted.SARS",
prefix.by.analysis = FALSE,gene.info = FALSE)
sars <- AddAnalysis(sars,"restricted.Mock",mock.tab)
sars <- AddAnalysis(sars,"restricted.SARS",sars.tab)
Analyses(sars) [1] "kinetics.Mock" "kinetics.SARS" "total.1h vs no4sU.Mock"
[4] "total.2h vs no4sU.Mock" "total.3h vs no4sU.Mock" "total.4h vs no4sU.Mock"
[7] "total.1h vs no4sU.SARS" "total.2h vs no4sU.SARS" "total.3h vs no4sU.SARS"
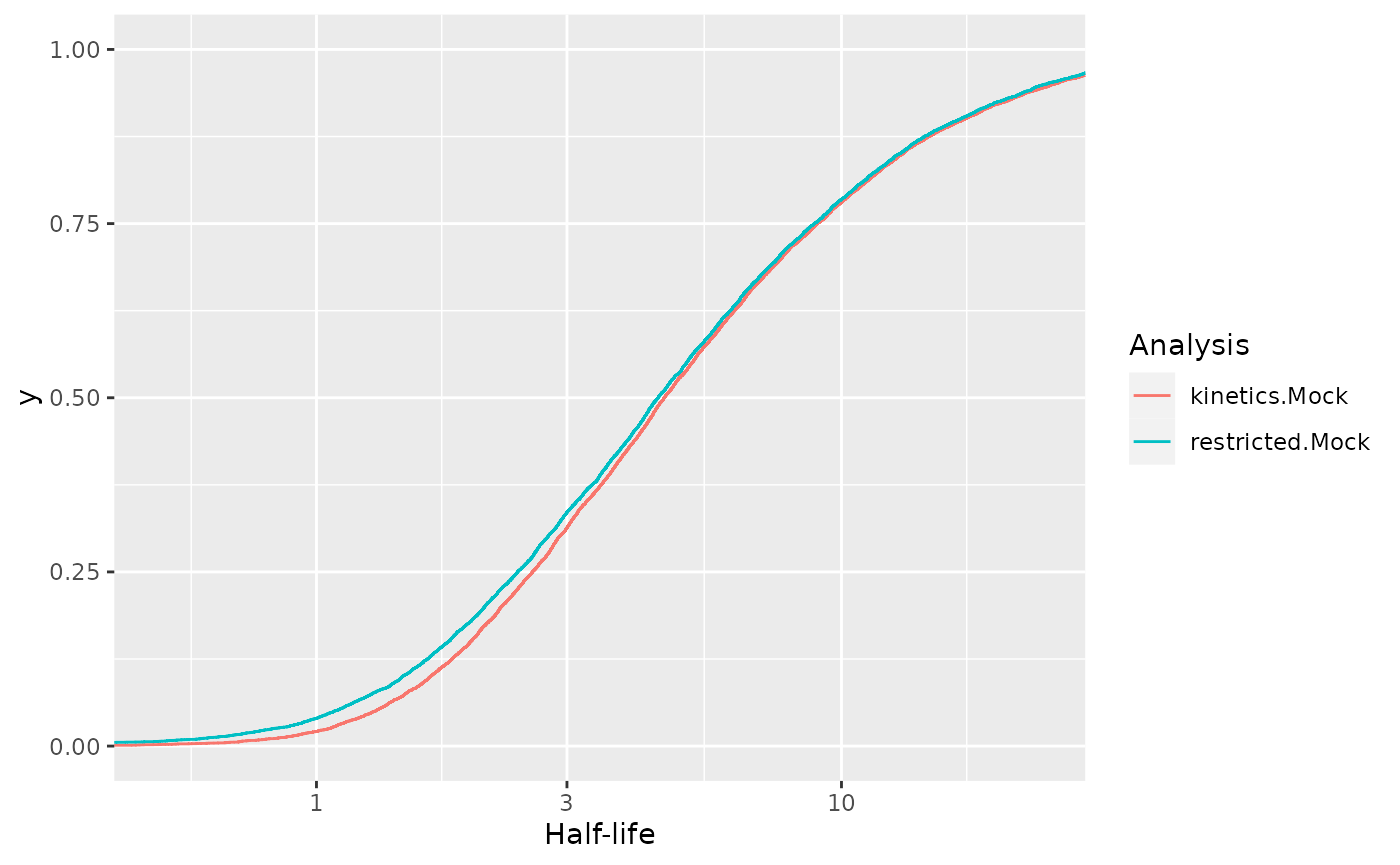
[10] "total.4h vs no4sU.SARS" "restricted.Mock" "restricted.SARS" Now we want to compare the distributions of half-lives with and
without removing the 1h timepoint. This can be accomplished by using the
by.row parameter
df <- GetAnalysisTable(sars,c("kinetics.Mock","restricted.Mock"),
columns = "Half-life",by.rows = TRUE)
rbind(head(df,4),tail(df,4)) Gene Symbol Length Type Analysis Half-life
1 ENSG00000197530 MIB2 4247 Cellular kinetics.Mock 6.685331
2 ENSG00000117859 OSBPL9 4520 Cellular kinetics.Mock 8.936141
3 ENSG00000134717 BTF3L4 4703 Cellular kinetics.Mock 4.453564
4 ENSG00000157077 ZFYVE9 5194 Cellular kinetics.Mock 5.129308
18321 ENSG00000196924 FLNA 8486 Cellular restricted.Mock 16.850448
18322 ENSG00000013563 DNASE1L1 3008 Cellular restricted.Mock 9.819117
18323 ORF1ab ORF1ab 21290 Viral restricted.Mock 1.729493
18324 S S 3822 Viral restricted.Mock 1.585582Now we can directly create an ecdf plot from this using ggplot, and we see that there are significant changes for short half-lives:
ggplot(df,aes(`Half-life`,color=Analysis))+
stat_ecdf()+
scale_x_log10()+
coord_cartesian(xlim=c(0.5,24))